In this post, we will go over HTTP cookies, their function and various types.

Cookies!
HTTP Cookies
Cookie is a small piece of data sent from a website to the user’s computer that contains some metadata about the user e.g. language and session in order to provide a better browsing experience. Cookies are typically used for three purposes:
-
Session Management: Storing login information, shopping carts and other such data.
-
Personalization: Color, language and theme settings.
-
Tracking: Analyzing user pattern and behavior.
In browsers such as Chrome, cookies are stored as an entry in the SQLite database file. Below is a general cookie structure. Examples of attribute include HTTP only, Secure etc.
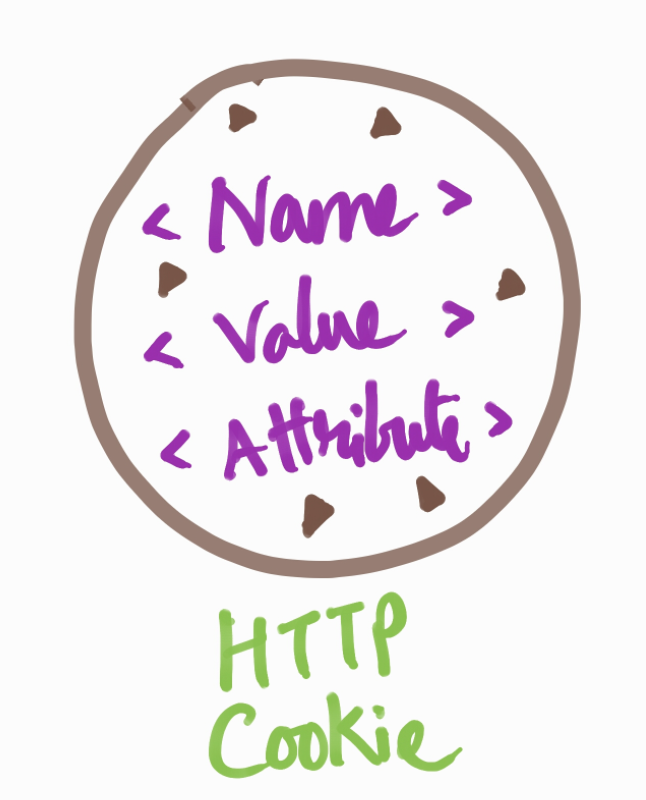
Cookie structure
Baking HTTP Cookies
We all have seen the cookie policy notification while browsing certain websites.
Cookie policy
This is more frequent on websites that allow purchases in order to store sessions. For instance, if you place certain items in Amazon shopping cart, close the browser and come back, the items still persist.
In the background, when a user visits the website, the server places a Set-Cookie header in the HTTP response. Here’s an example.
HTTP/1.0 200 OK
Content-type: text/html
Set-Cookie: user_lang=French
Set-Cookie: user_city=Paris
[page content]
In the above example, user_lang and user_city are the cookie names whereas French and Paris are the respective values. The server may place one or multiple cookie headers at the same time. This way, when the user visits the website again, the server can set the page contents in French and apply localization setting to better suit the user needs.
Types of HTTP Cookies
Just as cookies come in a variety of flavors from vanilla to spearmint, HTTP cookies are no different. Here are some of them.
- Secure cookie: Transmitted over HTTPS only.
- Supercookie: A cookie with a Top Level Domain (TLD) such as .com, .net etc.
- Session cookie: Exists only in the temporary memory while the user navigates the website.
- Third-party cookie: Ads storing cookies through a legitimate website.
- Zombie cookie: A cookie that gets recreated after deletion.
Of course, cookies have disadvantages too. Attackers can hijack a cookie and steal user data or drop a malicious cookie into the user’s system and track their activities. Read more about it here.